Accelerating Development of GLP-1 & GLP-2 Therapeutics with Validated Bioassays
Glucagon-like peptides, GLP-1 & GLP-2, are well-researched, metabolically significant peptide hormones secreted from the L-cells of the small intestine in response to diet. GLP-1 is crucial for glucose metabolism as it promotes insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner and drives anorexic effects via slow gastric emptying. It is hence a well-established target for Type 2 diabetes mellitus and weight loss. On the other hand, GLP-2 is a therapeutic target for inflammatory and short bowel syndrome demonstrated to play a protective role in reducing bone resorption by increasing bone mass. GLP-2 and analogs are emerging targets for the treatments of short bowel syndrome, Crohn’s disease, and osteoporosis. Both GLP-1 & -2 bind to respective receptors (GLP-1R & -2R) that are considered key metabolic targets for developing therapeutics for globally prevalent metabolic and gastrointestinal disorders. Several other novel GLP analogs, including biosimilars and biobetters are in clinical development; however, existing assays for characterizing their mechanism of action (MOA) are complex and require extensive development time.
Employing Eurofins DiscoverX Cell-Based Assays for GLP-1 & -2 and Related Targets
Eurofins DiscoverX® offers a comprehensive portfolio of functional cell-based assays for GLP-1 & -2, glucagon, gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP), insulin, and other targets associated with metabolic, gastrointestinal, and other related pathways. These assays enable the measurement of diverse MOAs (see Figure 1.) including GPCR second messenger (cAMP or calcium) accumulation; GPCR β-arrestin recruitment and internalization; and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) dimerization, phosphorylation, and SH2 recruitment assays.
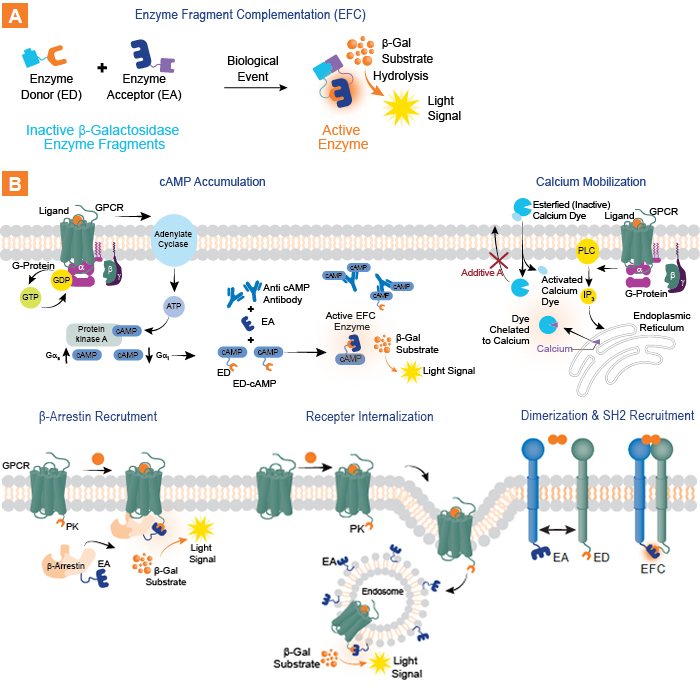
Figure 1. Functional, cell-based assay formats for GPCRs and RTKs involved in glucose metabolism. A. The proprietary Eurofins DiscoverX EFC technology is based on a split β galactosidase (β gal) enzyme. Enzyme activity is measured with addition of detection reagent containing luminescent enzyme substrate and detecting the complementation of the ED and EA fragments. B. A variety of functional assay formats for drug targets involved in regulation of glucose metabolism including cell lines and bioassays that evaluate multiple drug MOAs for important targets in the glucagon receptor family, including GLP-1R, GLP-2R, GIPR, and GCGR. Assays are available to evaluate activation of second messenger pathways (e.g. cAMP and Ca2+), β-arrestin recruitment, receptor internalization, and RTK (insulin receptor) dimerization, phosphorylation, and SH2 recruitment.
Eurofins DiscoverX’s cell-based assays are developed from stable cell lines enabling a continuous culture of cells applicable for screening and pre-clinical drug target discovery. The cell lines are further optimized into ready-to-use (RTU) bioassay kits that are highly reproducible, easy to perform, homogeneous, MOA reflective, and robust. These assay formats eliminate cell culture steps and help to accelerate development times by up to 12 months. In an effort to support the assays to be readily implemented in potency testing programs, clinically approved drugs have been used to qualify assays (e.g. semaglutide for GLP-1R), to make them fit-for-purpose for transferring to GMP (good manufacturing practice) labs for potency lot release testing.
For the development of GLP-1 & -2 and other target-specific analogs intended for commercial release, the Eurofins DiscoverX assay platform offers phase-appropriate formats with end-to-end support for every development program all the way to accelerated QC lot release testing.
Validation of GLP-1 & -2 Bioassays
It is imperative for developed assays to be suited for their intended purpose, and hence necessary to validate the operating characteristics and critical parameters such as accuracy, repeatability, and linearity of the assay (Figure 2.). Assay/method validation in turn makes the assay fit-for-use in the measurement of a drug’s relative potency. Eurofins BioPharma Testing Italy (BPT) has conducted a series of tests to validate both GLP-1 & -2 bioassays.
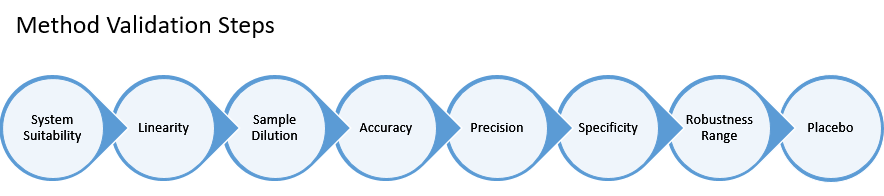
Figure 2. Steps involved in method validation. Established sequence of method validation based on setting a system suitability criteria for ensuring compliance and testing of critical parameters including linearity, accuracy, precision, and more related to the nature of the drug target.
Results of GLP-1 & -2 Bioassays Validation
Both cAMP Hunter™ GLP-1 Bioassay and PathHunter® CHO-K1 GLP-2 bioassays were validated using a series of method validations including a systematic testing of parameters typically identified as acceptable for assay performance. A system suitability criteria was first set to ensure each testing performed at the Eurofins BPT facility was compliant, followed by assessments of specified range of linearity and sample dilutions aligned with the nature of the analog/drug. Specific parameters such as specificity, accuracy, and precision were then challenged during each validation applicable to each quantitative bioassay testing.
For the GLP-1 & -2 bioassays, sample dilutional linearity when using a positive control as well as a United States Pharmacopeia (USP) reference standard, showed excellent R2 of 0.99. The relative potency tested under a range of nominal concentrations reflected on the assays being highly accurate. Assay repeatability and intermediate precision (involving different analysts and different days of testing) presented with excellent outcomes as well. Testing of these parameters resulted in confirming the robustness of the GLP-1 & -2 bioassays. Table 1 shows results of assay validation for each parameter corresponding to their acceptance and suitability criteria set for the bioassays.
| Parameter | System Suitability and Acceptance Criteria | GLP-1 Bioassay | GLP-2 Bioassay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specificity | Average of RLU Blank values ≤ RLU average of cells treated with lowest concentration of exponential phase of the curve | Pass | Pass |
| Agonist | GLP-1 & -2 agonist should have dose dependent effect | Pass | Pass |
| Linearity | R2 ≥ 0.98 and R ≥ 0.98 | R2 = 0.98 | R2 = 0.98 |
| Accuracy | 80% ≤ GLP-1 recovery % ≤ 125%, and 70% ≤ GLP-2 recovery % ≤ 130% | R2 = 0.98 | R2 = 0.98 |
| Precision | CV% of EC50 values should be less than or equal to 30% | Repeatability = 15% Intermediate = 27% |
Repeatability = 9% Intermediate = 30% |
| Robustness | Luminescence reading has been performed at 30 minutes and no EC50 variations should be observed | -10% ≤ EC50 T0 ≤ +10% |
-10% ≤ EC50 T0 ≤ +10% |
Table 1. Results of validation of GLP bioassays. A series of method validation testing parameters for both GLP-1 & -2 bioassays showed excellent R2 values for linearity and accuracy, including high repeatability and robustness.
Validation for both GLP-1 & -2 bioassays showed accurate, precise, specific, and robust results. The cAMP Hunter Liraglutide Bioassay Kit can be used to determine the potency of Liraglutide drug product to be released, via measurement of cellular cAMP levels that, in turn, reflects GLP-1R activation. The PathHunter CHO-K1 GLP-2R Bioassay can be used to determine the potency of GLP-2 agonists for treating adult patients deficient of GLP-2R activation by monitoring β-arrestin recruitment as a readout of receptor activation.
Conclusions
With the development of functional cell-based assays followed by validation runs, GLP-1 & -2 analogs intended for commercial release can utilize Eurofins DiscoverX’s assay platforms for characterization through QC lot release of drug candidates. Evaluating both GLP-1 & -2 for a complete understanding of therapeutic MOAs with different readouts, coupled with a reliable end-to-end support, can help reduce development times by months and accelerate lot release testing programs. Partnering with Eurofins BPT helps gain support on assay validation in addition to supporting development of biologics from analytical method development to marketed product release analysis with increased capacity.
Resources
- Evaluate GLP-1R targeted therapeutics using first-to-market semaglutide-qualified GLP-1R bioassay (Read Blog)
- Semaglutide GLP-1R Bioassay Kit (Catalog No. 95-0062Y2)
- PathHunter CHO-K1 GLP2R Bioassay Kit (Catalog No. 93-0572Y2)
- Related Products: Exendin-4 Bioassay kit, GLP1 (7-37) Bioassay Kit
- cAMP Detection Solutions for Small Molecules and Biologics (discoverx.com/camp-assays)
- Bioassay Kits (discoverx.com/bioassays)
